Data is a collection of facts, figures, objects, symbols, and events from different sources. Organizations collect data using various methods to make better decisions. Without data, it would be difficult for organizations to make appropriate decisions, so data is collected from different audiences at various times.
For example, an organization must collect data on product demand, customer preferences, and competitors before launching a new product. If data is not collected beforehand, the organization’s newly launched product may fail for many reasons, such as less demand and inability to meet customer needs.
Although data is a valuable asset for every organization, it does not serve any purpose until it is analyzed or processed to achieve the desired results.
What are Data Collection Methods?
Data collection methods are techniques and procedures for gathering information for research purposes. They can range from simple self-reported surveys to more complex quantitative or qualitative experiments.
Some common data collection methods include surveys, interviews, observations, focus groups, experiments, and secondary data analysis. The data collected through these methods can then be analyzed to support or refute research hypotheses and draw conclusions about the study’s subject matter.
Understanding Data Collection Methods
Data collection methods encompass a variety of techniques and tools for gathering quantitative and qualitative data. These methods are integral to the data collection and ensure accurate and comprehensive data acquisition.
Quantitative data collection methods involve systematic approaches, such as
- Numerical data,
- Surveys, polls and
- Statistical analysis
- To quantify phenomena and trends.
Conversely, qualitative data collection methods focus on capturing non-numerical information, such as interviews, focus groups, and observations, to delve deeper into understanding attitudes, behaviors, and motivations.
Combining quantitative and qualitative data collection techniques can enrich organizations’ datasets and gain comprehensive insights into complex phenomena.
Effective utilization of accurate data collection tools and techniques enhances the accuracy and reliability of collected data, facilitating informed decision-making and strategic planning.
Learn more about what is Self-Selection Bias, methods & its examples
Importance of Data Collection Methods
Data collection methods play a crucial role in the research process as they determine the quality and accuracy of the data collected. Here are some major importance of data collection methods.
- Quality and Accuracy: The choice of data collection technique directly impacts the quality and accuracy of the data obtained. Properly designed methods help ensure that the data collected is error-free and relevant to the research questions.
- Relevance, Validity, and Reliability: Effective data collection methods help ensure that the data collected is relevant to the research objectives, valid (measuring what it intends to measure), and reliable (consistent and reproducible).
- Bias Reduction and Representativeness: Carefully chosen data collection methods can help minimize biases inherent in the research process, such as sampling or response bias. They also aid in achieving a representative sample, enhancing the findings’ generalizability.
- Informed Decision Making: Accurate and reliable data collected through appropriate methods provide a solid foundation for making informed decisions based on research findings. This is crucial for both academic research and practical applications in various fields.
- Achievement of Research Objectives: Data collection methods should align with the research objectives to ensure that the collected data effectively addresses the research questions or hypotheses. Properly collected data facilitates the attainment of these objectives.
- Support for Validity and Reliability: Validity and reliability are essential to research validity. The choice of data collection methods can either enhance or detract from the validity and reliability of research findings. Therefore, selecting appropriate methods is critical for ensuring the credibility of the research.
The importance of data collection methods cannot be overstated, as they play a key role in the research study’s overall success and internal validity.
Types of Data Collection Methods
The choice of data collection method depends on the research question being addressed, the type of data needed, and the resources and time available. Data collection methods can be categorized into primary and secondary methods.
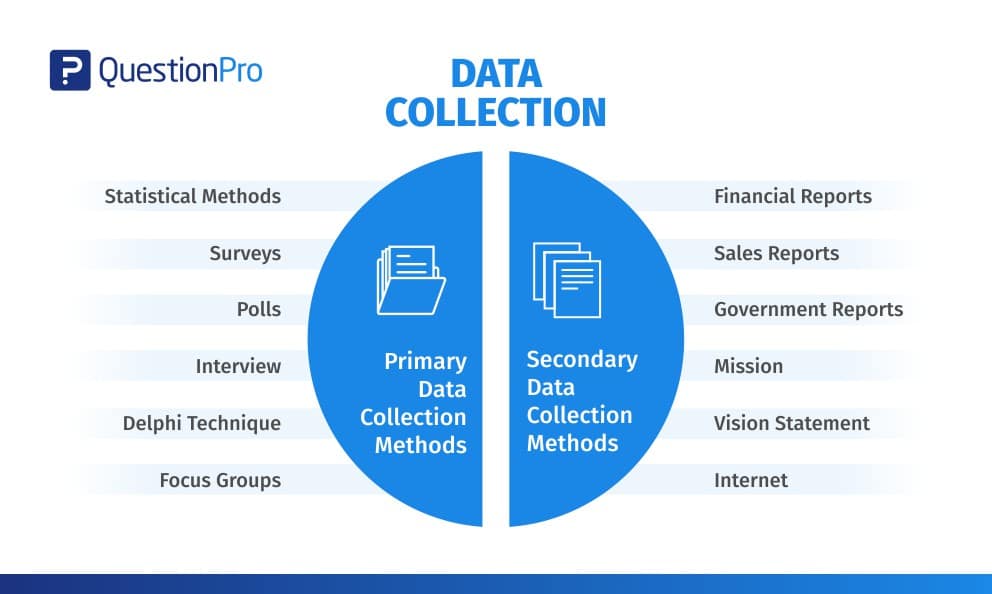
1. Primary Data Collection Methods
Primary data is collected from first-hand experience and is not used in the past. The data gathered by primary data collection methods are highly accurate and specific to the research’s motive.
Primary data collection methods can be divided into two categories: quantitative and qualitative.
Quantitative Methods:
Quantitative techniques for market research and demand forecasting usually use statistical tools. In these techniques, demand is forecasted based on historical data. These methods of primary data collection are generally used to make long-term forecasts. Statistical analysis methods are highly reliable as subjectivity is minimal.
- Time Series Analysis: A time series refers to a sequential order of values of a variable, known as a trend, at equal time intervals. Using patterns, an organization can predict the demand for its products and services over a projected time period.
- Smoothing Techniques: Smoothing techniques can be used in cases where the time series lacks significant trends. They eliminate random variation from the historical demand, helping identify patterns and demand levels to estimate future demand.The most common methods used in smoothing demand forecasting are the simple moving average and weighted moving average methods.
- Barometric Method: Also known as the leading indicators approach, researchers use this method to speculate future trends based on current developments. When past events are considered to predict future events, they act as leading indicators.

Qualitative Methods:
Qualitative data collection methods are especially useful when historical data is unavailable or when numbers or mathematical calculations are unnecessary.
Qualitative research is closely associated with words, sounds, feelings, emotions, colors, and non-quantifiable elements. These techniques are based on experience, judgment, intuition, conjecture, emotion, etc.
Quantitative methods do not provide the motive behind participants’ responses, often don’t reach underrepresented populations, and require long periods of time to collect the data. Hence, it is best to combine quantitative methods with qualitative methods.
1. Surveys: Surveys collect data from the target audience and gather insights into their preferences, opinions, choices, and feedback related to their products and services. Most survey software offers a wide range of question types.
You can also use a ready-made survey template to save time and effort. Online surveys can be customized to match the business’s brand by changing the theme, logo, etc. They can be distributed through several channels, such as email, website, offline app, QR code, social media, etc.
You can select the channel based on your audience’s type and source. Once the data is collected, survey software can generate reports and run analytics algorithms to discover hidden insights.
A survey dashboard can give you statistics related to response rate, completion rate, demographics-based filters, export and sharing options, etc. Integrating survey builders with third-party apps can maximize the effort spent on online real-time data collection.
Practical business intelligence relies on the synergy between analytics and reporting, where analytics uncovers valuable insights, and reporting communicates these findings to stakeholders.

Post a Comment